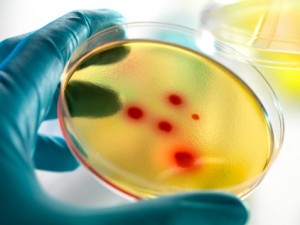
Bacterial contamination is a major concern for platelets, which limits platelet storage and availability. Platelets are currently stored at room temperature for up to 5 days.
The National Health Service Blood and Transplant of the United Kingdom recently conducted a randomized non-inferiority trial comparing platelets stored for 2- to 5-days versus 6- to 7-days in 122 adult thrombocytopenic hematology patients. After bacterial screening, researchers found no evidence that platelets stored for 2- to 5-days were superior to platelets stored for 6- to 7-days in stable hematology patients. Seventy-one percent of transfusions with platelets stored 2- to 5-days (mean=3.8 days, SD=1.0) were successful compared to 69% of transfusions for platelets stored 6- to 7-days (mean=6.4 days, SD=0.5)). The mean corrected platelet count increments, the number of bleeding events, and the interval to the next transfusions were comparable in each group. Further research is needed to evaluate platelets stored for up to 7 days used for transfusions in trauma and surgery patients.
Reference
 Transfusion offers CME credit for this study! Log on at www.wileyhealthlearning.com/trf.
Transfusion offers CME credit for this study! Log on at www.wileyhealthlearning.com/trf.