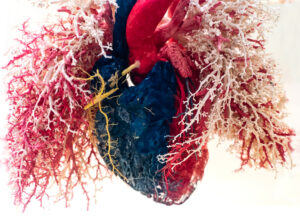
Over one million people undergo complex cardiac surgeries worldwide each year. Cardiac surgeries carry a considerable risk of postoperative bleeding and coagulation complications. During complex cardiac surgeries, fibrinogen levels and coagulation factor activities all decrease by about 40%. Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) and prothrombin complex concentrates (PCC) are the only recognized therapies for replacing the clotting factors that are lost during cardiac surgery, but few guidelines address dosing and timing of CCP. To better understand the safety profile of PCC in cardiac surgery patients, the Cochrane Collaboration identified 18 studies with a total of 4993 participants (two randomized controlled trials with 151 participants and 16 non-randomized trials) comparing PCC treatment to standard of care. They found that use of PCC may reduce the quantity of RBC transfusions and the incidence of RBC transfusions compared to standard treatment with either FFP or recombinant factor VIIa (rFV11a). In addition, they found no difference between the therapies in the number of thrombotic events, risk of mortality, risk of post-operative bleeding, or length of intensive care stay between treatments based on moderately-graded evidence. Additional research and randomized controlled trials are needed to evaluate the best treatments for coagulation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.
Reference: